Frontiers of Data and Computing ›› 2021, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 35-49.
doi: 10.11871/jfdc.10-1649.2021.06.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
PU Xiaorong1,*( ),HUANG Jiaxin1(
),HUANG Jiaxin1( ),LIU Junchi1(
),LIU Junchi1( ),SUN Jiayu2(
),SUN Jiayu2( ),LUO Jixiang1(
),LUO Jixiang1( ),ZHAO Yue1(
),ZHAO Yue1( ),CHEN Kecheng1(
),CHEN Kecheng1( ),REN Yazhou1(
),REN Yazhou1( )
)
Received:2021-11-15
Online:2021-12-20
Published:2022-01-26
Contact:
PU Xiaorong
E-mail:puxiaor@uestc.edu.cn;puxiaor@uestc.edu.cn;jiaxinhuang011403@gmail.com;jchiliu@163.com;sjy080512@163.com;galaxyluo@outlook.com;kennyZ96@hotmail.com;cs.ckc96@gmail.com;yazhou.ren@uestc.edu.cn
PU Xiaorong,HUANG Jiaxin,LIU Junchi,SUN Jiayu,LUO Jixiang,ZHAO Yue,CHEN Kecheng,REN Yazhou. A Survey on Clinical Oriented CT Image Denoising[J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(6): 35-49.
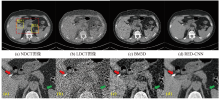
Fig.1
No. 263 paired NDCT and LDCT slice images of patient C002 from the LDCT-and Projection-data data set [52]. Two methods, BM3D and RED-CNN, are selected as the representatives of traditional methods and deep learning methods, respectively. The noise reduction results are compared through the two yellow ROI regions in the red dashed box: (a) NDCT; (b) LDCT; (c) The result of noise reduction using BM3D; (d) The result of noise reduction using RED-CNN."
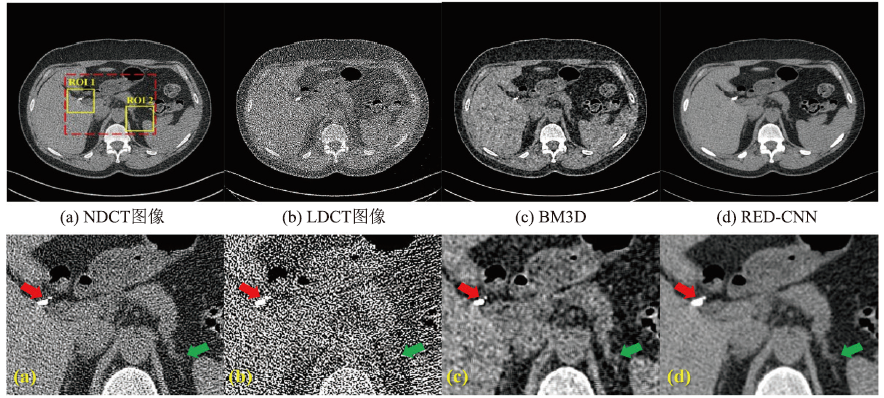
Table 1
Summary of representative CNN-Based LDCT image denoising methods between 2018-2021(In the table, PSNR is the peak signal-to-noise ratio, SSIM is the structural similarity, and RMSE is the root mean square error, which are commonly used in CT image evaluation)."
| 参考文献 | 噪声类型 | 应用场景 | 关键词 | 评价指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gholizadeh等 (2018) [ | 外加白噪声 | LDCT/X射线图像降噪 | 膨胀卷积 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Kadimesetty等 (2019) [ | 外加白噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 强化学习/批归一化 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Liu等 (2018) [ | 外加白噪声 | CT灌注图像降噪 | 遗传算法 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Han等(2018) [ | 真实噪声 | CT图像重建 | U-Net/跳跃连接 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Khoroushadi等(2019) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 小波变换 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Green等(2018) [ | 真实噪声 | 肺部超低剂量CT图像降噪 | 卷积神经网络 | PSNR\双盲评分 |
| Li等(2020) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 自注意力/自监督 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Hendriksen等(2020) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 自监督/无配对样本 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Wu等(2020)[ | 真实噪声 | CT灌注图像降噪 | 自监督/无配对样本 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Du等(2020)[ | 真实噪声 | 图像超分/LDCT图像降噪 | 无监督/域适应 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Chen等(2021)[ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 协同训练 | PSNR\双盲评分 |
| Chen等(2020)[ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | 构造成对伪样本 | PSNR\SSIM |
Table 2
Summary of representative GAN-Based LDCT image denoising methods between 2018-2021"
| 参考文献 | 噪声类型 | 应用场景 | 关键词 | 评价指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yu等 (2018) [ | 外加白噪声 | 光学相干层析成像降噪 | 深度网络/跳跃连接 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Abbasi等(2019) [ | 外加白噪声 | 3D-MRI/LDCT图像降噪 | 强化学习/全卷积网络 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Ma等(2018) [ | 真实噪声 | 光学相干层析成像降噪 | GAN/边缘优先 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| Hong等(2020) [ | 真实噪声 | CT图像重建 | CGAN/端到端网络 | PSNR\SSIM |
| Park等(2019) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | GAN/无监督 | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
| You等(2018) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | GAN/无监督 | PSNR\双盲评分 |
| Yang等(2018) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | WGAN/感知损失 | PSNR\双盲评分 |
| Zhang等(2021) [ | 真实噪声 | LDCT图像降噪 | U-Net | PSNR\SSIM\RMSE |
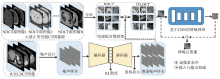
Fig.2
Deep learning framework based on LDCT image learning to extract noise [51]. The approximate noise samples extracted from real LDCT images are enhanced by an Encoder-Decoder. Then noise is randomly added to NDCT images to obtain paired pseudo LDCT / NDCT images. Finally, the constructed data set is used to train the noise reduction network based on CNN."
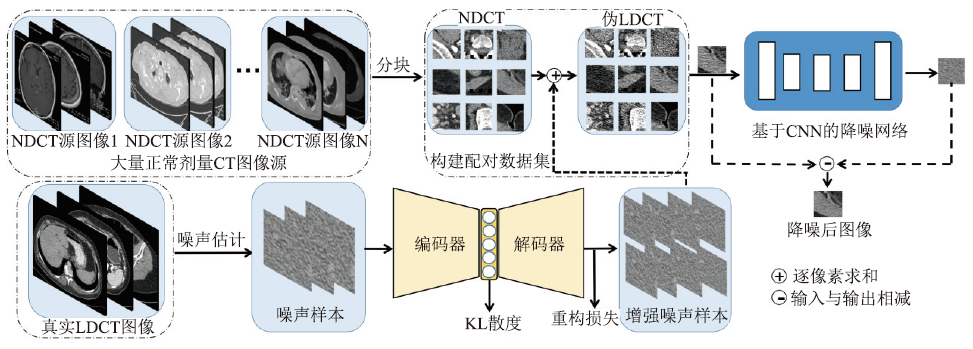
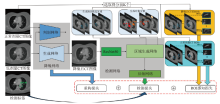
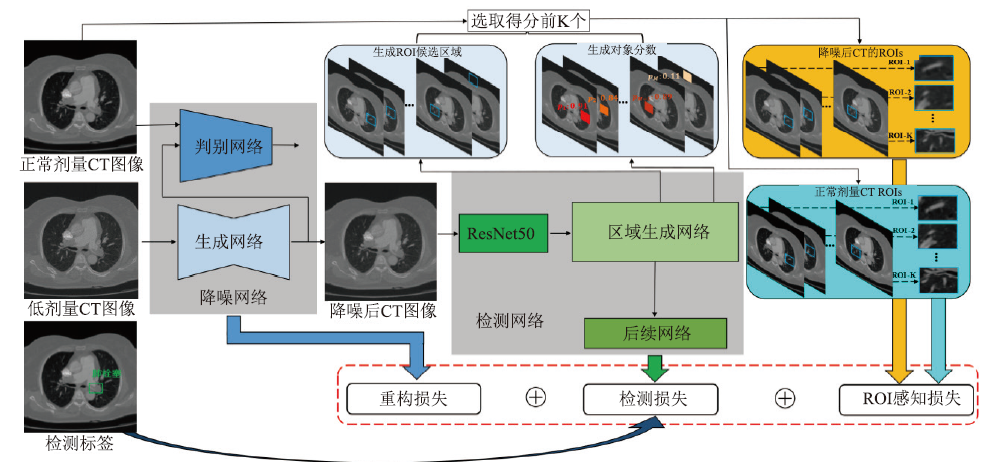
Fig.3
LDCT image denoising framework based on co-training[37]. The denoising networks includes a generator and discriminator. The denoised CT image is produced by the generator. The detection network includes the backbone network (ResNet50), the region proposal network (RPN), and the subsequent network. The ROI proposals and corresponding object scores are obtained by the RPN. According to the object score, the meaningful foreground ROIs in a denoised CT image and corresponding NDCT are selected for the computation of perceptual loss."
| [1] | Pan T. Computed Tomography: from Photon Statistics to Modern Cone-Beam CT[J]. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2009,50(7):1194. |
| [2] | 张秀文, 张永寿, 刘乃智. PET-CT工作原理及应用[J]. 中国医学装备, 2012, ( 11):22-25. |
| [3] | 石明国. 实用CT影像技术学[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1995: 233-235. |
| [4] | 朱兆丰. CT图像中噪声产生机理与维修[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2005,20(11):50-51. |
| [5] | Naidich D P, Marshall C H, Gribbin C, et al. Low-dose CT of the lungs: Preliminary observations[J]. Radiology, 1990,175(3):729-731. |
| [6] | 吴宁, 赵世俊. 积极规范地开展低剂量螺旋CT肺癌筛查[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2015(5):2. |
| [7] | Guo L, Chen Q, Shen Y, et al. Evaluation of a Low-Dose Computed Tomography Lung Cancer Screening Program in Henan, China[J]. JAMA Network Open, 2020,3(11):e2019039. |
| [8] | Shi J, Wang L, Wang S, Chen Y, et al. 2020. Applications of deep learning in medical imaging: a survey. Journal of Image and Graphics, 25(10):1953-1981. |
| [9] | Wang J, Lu H, Li T, et al. Sinogram noise reduction for low-dose CT by statistics-based nonlinear filters[C]. Image Processing pt.3, Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging, 2005,6(24):2058-2066. |
| [10] | Mileto A, Guimaraes L, Mccollough C, et al. State of the Art in Abdominal CT: The Limits of Iterative Recons-truction Algorithms[J]. Radiology, 2019,293(3):491-503. |
| [11] | Li M, Hsu W, Xie X, et al. SACNN: Self-Attention Con-volutional Neural Network for Low-Dose CT Denoising with Self-supervised Perceptual Loss Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020,39(7):2289-2301. |
| [12] | Hara A, Paden R, AC Silva, et al. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasi-bility study[J]. American Journal of Roentgenology, 2009,193(3):764-771. |
| [13] | Sidky E, Pan X. Image reconstruction in circular cone-beam computed tomography by constrained, total-variation minimization[J]. Physics in Medicine & Bio-logy, 2008,53(17):4777-4807. |
| [14] | Yang C, Gao D, Cong N, et al. Bayesian statistical recon-struction for low-dose X-ray computed tomography using an adaptive-weighting nonlocal prior[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging & Graphics, 2009,33(7):495-500. |
| [15] | Xu Q, Yu H, Mou X, et al. Low-dose X-ray CT reconstr-uction via dictionary learning[J]. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 2012,31(9):1682-1697. |
| [16] | Cai J, Jia X, Gao H, et al. Cine cone beam CT reconstruction using low-rank matrix factorization: algorithm and a proof-of-principle study[J]. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 2014,33(8):1581-1591. |
| [17] | Li Z, Yu L, Trzasko J D, et al. Adaptive nonlocal means filtering based on local noise level for CT denoising[J]. Medical physics, 2014,41(1):11908. |
| [18] | Feruglio P, Vinegoni C, Gros J, et al. Block matching 3D random noise filtering for absorption optical projection tomography[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2010,55(18):5401-5415. |
| [19] | Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhang W, et al. Low-dose CT den-oising with convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), 2017: 143-146. |
| [20] | Chen H, Zhang Y, Kalra M K, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 2017,36(12):2524-2535. |
| [21] | Mao X, Shen C, Yang Y. Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with sym-metric skip connections[C]. In Proceedings of the 30 th International Conference on Neural Information Proce-ssing Systems (NIPS’16) , 2016: 2810-2818. |
| [22] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE confe-rence on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016: 770-778. |
| [23] | Hu C, Zhang Y, Zhang W, et al. Low-dose CT via convo-lutional neural network[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017,8(2):679-694. |
| [24] | Yang Q, Yan P, Kalra M K, et al. CT image denoising with perceptive deep neural networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1702. 07019, 2017. |
| [25] | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR2015). https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. |
| [26] | 张雄, 杨琳琳, 上官宏 等. 基于生成对抗网络和噪声水平估计的低剂量CT图像降噪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021,43(8):2404-2413. |
| [27] | Gholizadeh-Ansari M, Alirezaie J, Babyn P. Low-dose CT Denoising with Dilated Residual Network[C]. 40 th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) , 2018: 5117-5120. |
| [28] | Kadimesetty V S, Gutta S, Ganapathy S, et al. Convo-lutional Neural Network-Based Robust Denoising of Low-Dose Computed Tomography Perfusion Maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2018,3(2):137-152. |
| [29] | Liu P, Li Y, Basha M, et al. Neural Network Evolution Using Expedited Genetic Algorithm for Medical Image Denoising[C]. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI, 2018: 12-20. |
| [30] | Han Y, Ye J. Framing U-Net via Deep Convolutional Fra-melets: Application to Sparse-View CT[J]. IEEE Tran-sactions on Medical Imaging, 2018,37(6):1418-1429. |
| [31] | Khoroushadi M, Sadegh M. Enhancement in low-dose computed tomography through image denoising techniques: Wavelets and deep learning[D]. Ph.D. thesis, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing. 2018. |
| [32] | Green M, Marom E, Konen E, et al. Learning Real Noise for Ultra-Low Dose Lung CT Denoising[C]. Patch-Based Techniques in Medical Imaging, 2018: 3-11. |
| [33] | Li M, Hsu W, X Xie, et al. SACNN: Self-Attention Con-volutional Neural Network for Low-Dose CT Den-oising with Self-supervised Perceptual Loss Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020,39(7):2289-2301. |
| [34] | Hendriksen A A, Pelt D M, Batenburg K J. Noise2Inverse: Self-supervised deep convolutional denoising for linear inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020,6:1320-1335. |
| [35] | Wu D, Ren H, Li Q. Self-supervised Dynamic CT Per-fusion Image Denoising with Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2021,5(3):350-361. |
| [36] | Du W, Chen H, Yang H. Learning Invariant Representa-tion for Unsupervised Image Restoration[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-nition (CVPR), 2020: 14471-14480. |
| [37] | Chen K, Long K, Ren Y, Sun J, Pu X. Lesion-Inspired Denoising Network: Connecting Medical Image Denoi-sing and Lesion Detection[C]. Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2021: 3283-3292. |
| [38] | Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Viergever M A, et al. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT[J]. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 2017,36(12):2536-2545. |
| [39] | Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-Image Tra-nslation with Conditional Adversarial Networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-nition (CVPR), 2017: 5967-5976. |
| [40] | Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Gene-rative Adversarial Networks[J]. Advances in Neural Infor-mation Processing Systems, 2014,3:2672-2680. |
| [41] | Burlina P M, Joshi N, Pekala M, et al. Automated grading of age-related macular degeneration from color fundus images using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. JAMA ophthalmology, 2017,135(11):1170-1176. |
| [42] | Maas A L, Hannun A Y, Ng A Y. Rectifier Nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]. In Proc. ICML, 2013,30(1):3. |
| [43] | Glorot X, Bengio Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks[C]. Procee-dings of the thirteenth international conference on artifi-cial intelligence and statistics. JMLR Workshop and Con-ference Proceedings, 2010: 249-256. |
| [44] | Yu A, Liu X, Wei X, et al. Generative Adversarial Netw-orks with Dense Connection for Optical Coherence Tomo-graphy Images Denoising[C]. 2018 11th Intern-ational Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), 2018: 1-5. |
| [45] | Abbasi A, Monadjemi A, Fang L, et al. Three-dim-ensional optical coherence tomography image denoising through multi-input fully-convolutional networks[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2019,108:1-8. |
| [46] | Ma Y, Chen X, Zhu W, et al. Speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography images based on edge-sensitive cGAN[J]. Biomedical optics express, 2018,9(11):5129-5146. |
| [47] | Hong Z, Fan X, Jiang T, et al. End-to-End Unpaired Image Denoising with Conditional Adversarial Networks[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelli-gence, 2020,34(4):4140-4149. |
| [48] | Park H S, Baek J, You S K, et al. Unpaired image denoi-sing using a generative adversarial network in X-ray CT[J]. IEEE Access, 2019,7:110414-110425. |
| [49] | You C, Yang Q, Shan H, et al. Structurally-sensitive Mul-ti-scale Deep Neural Network for Low-Dose CT Denoi-sing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018,6:41839-41855. |
| [50] | Yang Q, Yan P, Zhang Y, et al. Low-Dose CT Image De-noising Using a Generative Adversarial Network with Wasserstein Distance and Perceptual Loss[J]. IEEE Tran-sactions on Medical Imaging, 2018,37(6):1348-1357. |
| [51] | Chen K, Huang J, Sun J, et al. Task-Driven Deep Lear-ning for LDCT Image Denoising[C]. In The Fourth Inter-national Symposium on Image Computing and Digital Medicine. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2020: 35-39. |
| [52] | 段影影. 医学图像质量评价方法研究[D]. 广东:南方医科大学, 2010. |
| [53] | Shan H, Padole A, Homayounieh F, et al. Competitive performance of a modularized deep neural network com-pared to commercial algorithms for low-dose CT image reconstruction[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019,1(6):269-276. |
| [54] | 段影影, 马建华, 陈武凡, 等. 改进的结构相似医学图像质量评价方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2010,46(2):145-149. |
| [55] | 张剑华, 张自然, 汪晓妍, 等. 基于结构显著性的医学图像质量评价[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2015,43(6):636-641. |
| [56] | Virendra K, Gu Y, Satrajit B, et al. Radiomics: the pro-cess and the challenge[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012,30(9):1234-1248. |
| [57] | 陆锐, 何健, 周科峰, 等. 自动管电流调制扫描及ASIR重建下胸部CT噪声指数的优化[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2016,26(06):1012-1016. |
| [58] | Junior F, Raniery R, Koenigkam-Santos M, Cipriano F, et al. Radiomics-based features for pattern recognition of lung cancer histopathology and metastases[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018,159:23-30. |
| [59] | Zhang Q, Xiao Y, Suo J, et al. Sonoelastomics for Breast Tumor Classification: A Radiomics Approach with Clustering-Based Feature Selection on Sonoelastography[J]. Ultrasound in medicine & biology, 2017,43(5):1058-1069. |
| [60] | Coroller T, Grossmann P, Hou Y, et al. CT-Based radiomic signature predicts distant metastasis in lung adenocar-cinoma[J]. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 2015,114(3):345-350. |
| [61] | Visvikis D, Rest C, Jaouen V, et al. Artificial intelligence, machine (deep) learning and radio(geno)mics: definitions and nuclear medicine imaging applications[J]. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2019,46(13):2630-2637. |
| [1] | XU Songyuan,LIU Feng. ESDRec: A Data Recommendation Model for Earth Big Data Platform [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2023, 5(1): 55-64. |
| [2] | CHEN Qiong,YANG Yong,HUANG Tianlin,FENG Yuan. A Survey on Few-Shot Image Semantic Segmentation [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(6): 17-34. |
| [3] | HE Tao,WANG Guifang,MA Tingcan. Discovering Interdisciplinary Research Based on Word Embedding [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(6): 50-59. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yining,HE Hongbo,WANG Runqiang. A Survey on Popular Digital Audio Prediction Techniques [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(4): 81-92. |
| [5] | CHEN Zijian,LI Jun,YUE Zhaojuan,ZHAO Zefang. Hybrid Recommendation Model Based on Autoencoder and Attribute Information [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(3): 148-155. |
| [6] | XIAO Jianping,LONG Chun,ZHAO Jing,WEI Jinxia,HU Anlei,DU Guanyao. A Survey on Network Intrusion Detection Based on Deep Learning [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(3): 59-74. |
| [7] | LI Xu,LIAN Yifeng,ZHANG Haixia,HUANG kezhen. Key Technologies of Cyber Security Knowledge Graph [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(3): 9-18. |
| [8] | ZHAO Weiyu,ZHANG Honghai,ZHONG Bo. A Deep Learning Based Method for Remote Sensing Image Parcel Segmentation [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2021, 3(2): 133-141. |
| [9] | SHEN Biao,CHEN Yang,YANG Chen,LIU Bowen. Computer Vision Detection and Analysis of Mesoscale Eddies in Marine Science [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2020, 2(6): 30-41. |
| [10] | Ren Huiying,Wang Jing,Wang Yangang. Turbulence Modeling Based on AutoML [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2020, 2(4): 121-131. |
| [11] | Zhang Shenglin,Lin Xiaofei,Sun Yongqian,Zhang Yuzhi,Pei Dan. Research on Unsupervised KPI Anomaly Detection Based on Deep Learning [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2020, 2(3): 87-100. |
| [12] | Chen Lei,Yuan Yuan. Image Recognition of Agricultural Diseases Based on Deep Transfer Learning [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2020, 2(2): 111-119. |
| [13] | Liu Chenglin. Document Image Recognition: Retrospective and Perspective of Technology [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2019, 1(2): 17-25. |
| [14] | Yu Yizhou, Ma Jiechao, Shi Dejun, Zhou Zhen. Application of Deep Learning in Medical Imaging Analysis: A Survey [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2019, 1(2): 37-52. |
| [15] | Yanjun Ma,Dianhai Yu,Tian Wu,Haifeng Wang. PaddlePaddle: An Open-Source Deep Learning Platform from Industrial Practice [J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2019, 1(1): 105-115. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
